| |
Links to sites with Organic Molecule models and diagrams
Molecular Model Visualization SW - RasMol Home Page
http://www.umass.edu/microbio/rasmol/
Other modelers
http://valhalla.chem.udel.edu/3-D.html
Molecular Viewers and Drawing Programs
http://ep.llnl.gov/msds/dvc/viewrs.html
a) Alcohols (5 structural, 4 Lewis) are compounds which have one (or
more) -OH group(s) attached to a carbon.
Some of the alcohols below have isomers in which there is no -OH group. These
"non-OH" structures are not alcohols, so do not include them here.
|
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
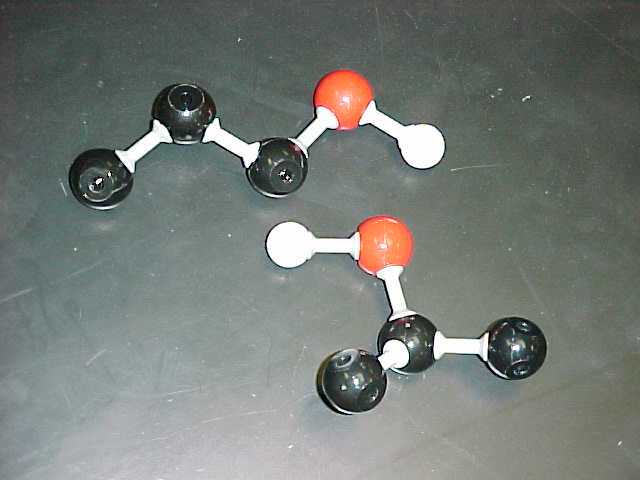
methanol, (also called methyl alcohol) |
ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol) |
|
CH3OH |
C2H5OH |
|
|
 |
|
propanol, (also called propyl alcohol)
|
butanol,(also called butyl alcohol) |
|
C3H7OH |
C4H9OH |
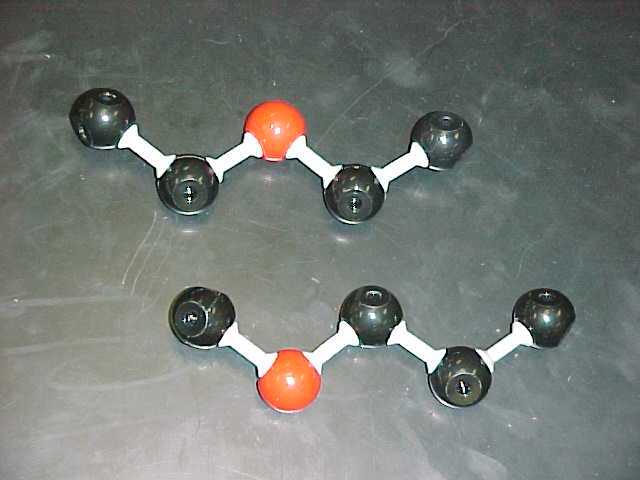
b) Ethers (4 structural, 2 Lewis)
are substances which contain an oxygen which is itself bonded to two other
carbons.
Any substance which contains a C-O-C arrangement in it is considered an ether.
|
 |
 |
|
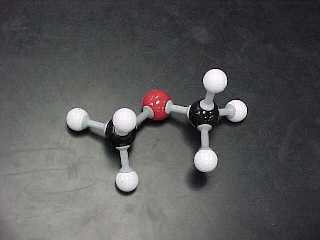
dimethyl ether |
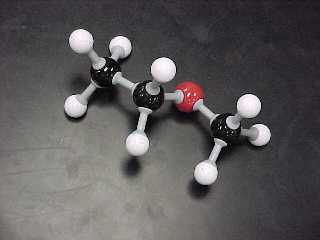
methyl ethyl ether |
|
CH3OCH3 |
CH3OC2H5 |
|

|
|
|
diethyl ether |
|
|
C2H5OC2H5
|
|
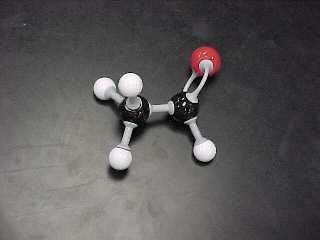
c) Aldehydes (2 structural, 2 Lewis)
are substances that have a double bonded oxygen
connected to a
TERMINAL carbon (the end carbon in a chain).
There also MUST be
a hydrogen connected to the terminal carbon.
|
 |
 |
|
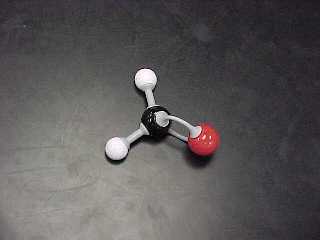
methanal, (also called formaldehyde) |
ethanal, (also called acetaldehyde) |
|
CH2O |
CH3CHO |
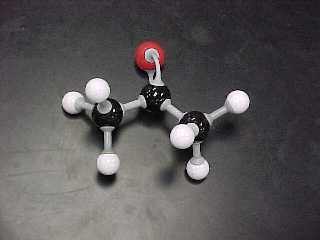
d) Ketones (1 structural, 1 Lewis) are substances that have an oxygen
double bonded to a carbon and the carbon is NOT a terminal carbon.
|
 |
|
acetone, |
|
CH3COCH3 |
|
|
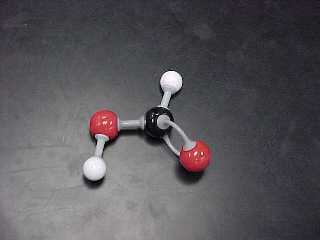
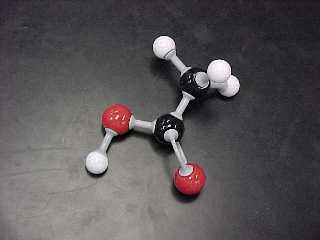
e) Acids (2 structural, 2 Lewis) are substances that have two atoms
attached to a terminal carbon: a double bonded oxygen AND an -OH group.
Both are attached to the SAME carbon.
|
 |
 |
|
methanoic acid (also known as formic acid) |
ethanoic acid (also known as acetic acid) |
|
HCOOH |
CH3COOH |
DAY 1
a) Alkane (7 structural, 3 Lewis) is the category name for a set
of compounds which contain
carbon and hydrogen and ONLY single bonds. An alkane has the general formula of CnH2n + 2. Build the
following alkanes:
|
methane, CH4
 |
ethane, C2H6
 |
|
propane, C3H8
 |
butane, C4H10
&
pentane, C5H12
 |
|
hexane, C6H14
& eptane, C7H16
 |
|
|
Special Note: there are
TWO (or more) different ways to make
some structures, starting with the C4H10
formula. |
Alkene (3 structural, 2 Lewis) is the category name for a set of
compounds which contain carbon and hydrogen, ONE double bond and the rest
single bonds. An alkene has the general formula of CnH2n.
|
ethene (also called ethylene), C2H4

|
propene (also called propylene), C3H6
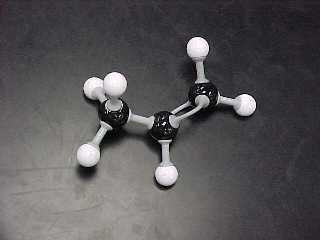
|
|
butene (also called butylene), C4H8
 |
|
Special Note: Butene
can have the double bond in two different locations.
Alkyne (3 structural, 2 Lewis) is the category name for a
set of compounds which contain carbon and hydrogen,
ONE triple bond and the
rest single bonds. An alkyne has the general formula of CnH2n
- 2. Pronounce alkyne to rhyme with "nine."
|
ethyne (also called acetylene), C2H2
 |
propyne, C3H4
 |
|
butyne, C4H6
 |
|
Special Note: Butyne can have the triple
bond in two different locations. |
DAY 4
a) Cycloalkanes are compounds which have only carbon and hydrogen
with ONLY single bonds. However, there is a twist - the carbons are
connected in a circular (it's called a ring) manner. The carbons are NOT in
a straight chain, but rather the two "ends" of a straight chain are
connected to each other. (Please use the thinner bonds to make the carbon to
carbon single bonds in cyclopropane.) Build the following models:
1. cyclopropane, C3H6
A picture of cyclopropane
2. cyclobutane, C4H8
A picture of cyclobutane
3. cyclopentane, C5H10
A picture of cyclopentane
4. cyclohexane, C6H12
A picture of cyclohexane
b) Cycloalkenes are compounds which have only carbon and hydrogen
with ONLY one double bond and the rest single bonds. Remember, cyclo- means
that the carbons are connected in a ring manner. Do NOT draw the carbons in
a straight chain. (Please use the thinner bonds to make the carbon to carbon
single bonds in cyclopropene.) Build the following models:
5. cyclopropene, C3H4
A picture of cyclopropene
6. cyclobutene, C4H6
A picture of cyclobutene
7. cyclopentene, C5H8
A picture of cyclopentene
8. cyclohexene, C6H10
A picture of cyclohexene
|